Embark on a culinary journey with the lacto vegetarian diet plan, a nourishing approach that combines the goodness of dairy with the vibrant flavors of plant-based foods. Discover the health benefits, nutritional considerations, and practical tips to make this lifestyle a fulfilling and sustainable choice.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essence of a lacto vegetarian diet, exploring its principles, potential drawbacks, and evidence-based research supporting its health claims. Prepare to be inspired by a sample meal plan that showcases the diversity and deliciousness of this plant-forward eating style.
Lacto Vegetarian Diet Overview
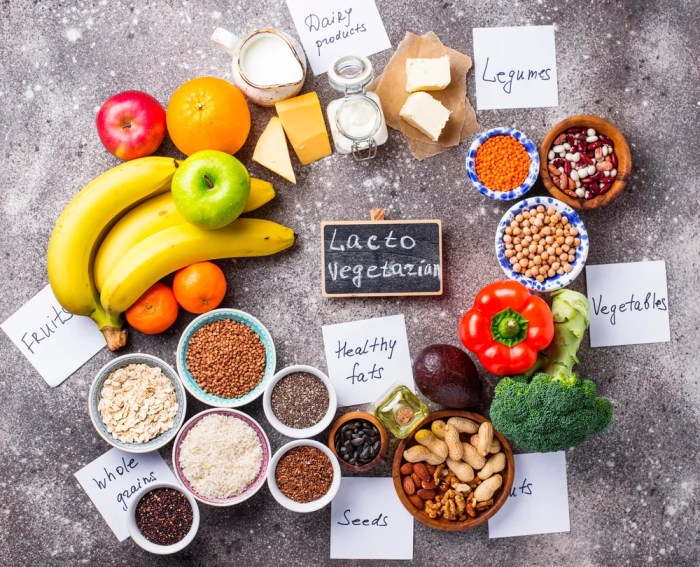

A lacto vegetarian diet is a type of vegetarian diet that includes dairy products but excludes meat, poultry, fish, and eggs. This diet is based on the belief that consuming dairy products is beneficial for health and that avoiding animal products is ethical.
Lacto vegetarians typically consume a variety of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. They also include dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter, in their diet.
Typical Foods Consumed, Lacto vegetarian diet plan
- Fruits: apples, bananas, berries, citrus fruits, melons
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, celery, leafy greens, tomatoes
- Legumes: beans, lentils, peas
- Nuts: almonds, cashews, peanuts, walnuts
- Seeds: chia seeds, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
- Whole grains: brown rice, oatmeal, quinoa, whole-wheat bread
- Dairy products: milk, yogurt, cheese, butter
Nutritional Considerations

A lacto vegetarian diet offers an array of nutritional benefits. It is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products, providing a diverse range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
However, certain nutrient deficiencies may arise, such as vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products. Lacto vegetarians can address this by consuming fortified foods or taking supplements.
As a vegetarian, eating healthy requires some planning. To ensure you’re getting all the essential nutrients, consider reading this guide that provides practical tips on incorporating protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12 into your diet. By following these recommendations, you can enjoy a nutritious and balanced vegetarian lifestyle.
Protein Intake
Adequate protein intake is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, repairing tissues, and producing enzymes and hormones. Plant-based sources of protein include legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products. Lacto vegetarians can supplement their protein intake by consuming dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese.
Health Implications
Adopting a lacto vegetarian diet offers a plethora of health benefits, including a reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved overall well-being. Studies have shown that individuals who adhere to this dietary pattern experience a lower risk of developing cardiovascular ailments, certain types of cancer, and obesity.
Embarking on a vegetarian journey can be a delicious and nutritious endeavor. By embracing plant-based foods, you’ll not only be reducing your environmental footprint but also fueling your body with an abundance of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. If you’re new to vegetarianism, check out our comprehensive guide on how to eat healthy as a vegetarian to ensure you’re getting all the essential nutrients you need.
One of the primary benefits of a lacto vegetarian diet is its positive impact on heart health. The consumption of plant-based foods, rich in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, helps lower cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve blood pressure regulation. These factors collectively contribute to a decreased risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Potential Drawbacks and Mitigation
While a lacto vegetarian diet offers numerous health advantages, it is essential to be aware of potential drawbacks and limitations. One potential concern is the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, as this vitamin is primarily found in animal products. To mitigate this risk, individuals following a lacto vegetarian diet should ensure adequate intake of vitamin B12-fortified foods or supplements.
Another potential limitation is the reduced protein intake compared to non-vegetarian diets. However, plant-based protein sources, such as legumes, tofu, and tempeh, can provide sufficient protein when consumed in combination throughout the day. Including a variety of plant-based protein sources in the diet ensures the intake of all essential amino acids.
It is also crucial to note that a lacto vegetarian diet may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with specific dietary restrictions or allergies may need to make further modifications to their diet. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help personalize the diet to meet individual needs and preferences.
Evidence-Based Research
Numerous studies have provided evidence supporting the health claims associated with a lacto vegetarian diet. A comprehensive review of studies published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that vegetarians have a 24% lower risk of death from heart disease compared to non-vegetarians.
Another study, published in the International Journal of Cancer, reported that vegetarians have a 12% lower risk of developing all types of cancer, including a 20% lower risk of colorectal cancer and a 15% lower risk of prostate cancer.
Furthermore, a study published in the Journal of the American Dietetic Association found that lacto vegetarians have a lower body mass index (BMI) and a reduced risk of obesity compared to non-vegetarians.
These studies, among others, provide robust evidence supporting the health benefits associated with a lacto vegetarian diet, making it a viable option for individuals seeking to improve their overall health and well-being.
Tips for Success: Lacto Vegetarian Diet Plan
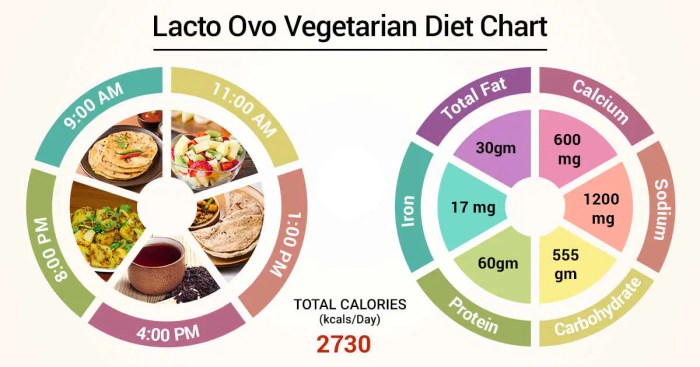
Embarking on a lacto vegetarian diet requires planning and dedication. To ensure a smooth transition and long-term adherence, consider the following tips:
Meal planning is crucial. Plan your meals ahead of time to avoid impulsive choices. Include a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups, ensuring adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Reading Food Labels
Reading food labels is essential to identify hidden animal products. Pay attention to the ingredient list and nutrition facts panel, checking for ingredients such as whey, casein, or gelatin.
Finding Support
Surrounding yourself with like-minded individuals can provide invaluable support and motivation. Join online communities, connect with local vegetarian groups, or consult with a registered dietitian specializing in plant-based diets.
Overcoming Challenges
Anticipate challenges and develop strategies to overcome them. If you experience cravings for meat or dairy, distract yourself with healthy snacks or engage in a non-food-related activity. Remind yourself of your reasons for adopting the diet and the potential health benefits.
Staying Motivated
Staying motivated requires a positive mindset and a focus on the benefits of the diet. Set realistic goals, celebrate your progress, and don’t be discouraged by occasional setbacks. Remember that a lacto vegetarian diet is a journey, not a destination.
Closing Notes
As you embrace the lacto vegetarian diet plan, remember that consistency and a positive mindset are key. With careful planning and support from like-minded individuals, you can unlock the transformative power of this nourishing approach. Embrace the flavors of nature, nurture your well-being, and embark on a culinary adventure that will leave you feeling energized, satisfied, and connected to your food.
Essential Questionnaire
Is the lacto vegetarian diet suitable for everyone?
While the lacto vegetarian diet can be a healthy choice for many, it may not be appropriate for individuals with certain health conditions or allergies. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to assess individual needs and ensure a balanced and nutritious diet.
Can I get enough protein on a lacto vegetarian diet?
Yes, it is possible to meet protein requirements on a lacto vegetarian diet. Plant-based sources of protein include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. Dairy products also contribute to protein intake. Combining different plant-based protein sources throughout the day helps ensure adequate intake.